What Is Addition Reaction Class 11
Test your knowledge on addition. All the atoms in the original molecules are found in the bigger one.

Reactions Of Alkenes A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
Nucleophilic addition reaction of alkynes is generally catalysed by the presence of heavy metal salts such as those of mercury and barium.

What is addition reaction class 11. All alkenes undergo addition reactions with the hydrogen halides. Here we will see the difference between oxidation and reduction reaction. The general equation for an addition reaction.
Can you explain this answer. Electrophilic addition mechanism is a chemical reaction between a nucleophile and an electrophile adding to triple or double bonds. EduRev Class 11 Question is disucussed on EduRev Study Group by 137 Class 11 Students.
Addition reactions are typical of unsaturated organic compoundsie alkenes which contain a carbon-to-carbon double bond and alkynes which have a carbon-to-carbon triple bondand. An electrophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction which happens because what we think of as the important molecule is attacked by an electrophile. Addition reactions occur with unsaturated compounds.
With but-2-ene you get 2-chlorobutane. It is also a fact that these are the balanced chemical reactions. If the answer is not available please wait for a while and a community member will probably answer this soon.
For example with ethene and hydrogen chloride you get chloroethane. A nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electron-deficient or electrophilic double or triple bond a π bond reacts with a nucleophile which is an electron-rich reactant with the disappearance of the double bond and creation of two new single or σ bonds. To be more precise an electrophilic addition reaction is the tendency to combine and react with chemical substances.
A Chemical reaction is the process in which one or more substances react and hence as a result then converted to one or more different substances. An addition reaction is a reaction in which two molecules join together to make a bigger one. Nothing is lost in the process.
You can study other questions MCQs videos and tests for Class 11 on EduRev and even discuss your questions like Consider the following addition reaction on a pure enantiomer of the shown bromoalkeneQ. Addition reactions are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds such as molecules with carboncarbon double bonds alkenes or with triple bonds alkynes and compounds that have rings which are also. Addition reaction any of a class of chemical reactions in which an atom or group of atoms is added to a molecule.
A B C. As a result the electron density in the triple bond gets considerably reduced and therefore the nucleophilic attack is. Notice that C is the final product with no A or B remaining as a residue.
Imagine that you are given two sets of wooden planks and asked to make something out of them - anything you want. A hydrogen atom joins to one of the carbon atoms originally in the double bond and a halogen atom to the other. An elimination reaction occurs when a reactant is broken up into two products.
Addition to symmetrical alkenes. The function of mercury ions Hg 2 or barium ions Ba 2 is to form 7r-complex by withdrawing the electron density from the -cloud. Elimination reactions occur with saturated compounds.
Each question has four choices a b c and d out of which ONLY ONE option is correctQWhat is the major addition product in the following reactionsabcdCorrect answer is option B. An addition reaction in organic chemistry is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one the adduct. Watch Ad Free Videos Completely FREE on Physicswallah Apphttpsbitly2SHIPW6Download the App from Google Play StoreDownload Lecture Notes From Phy.

Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism
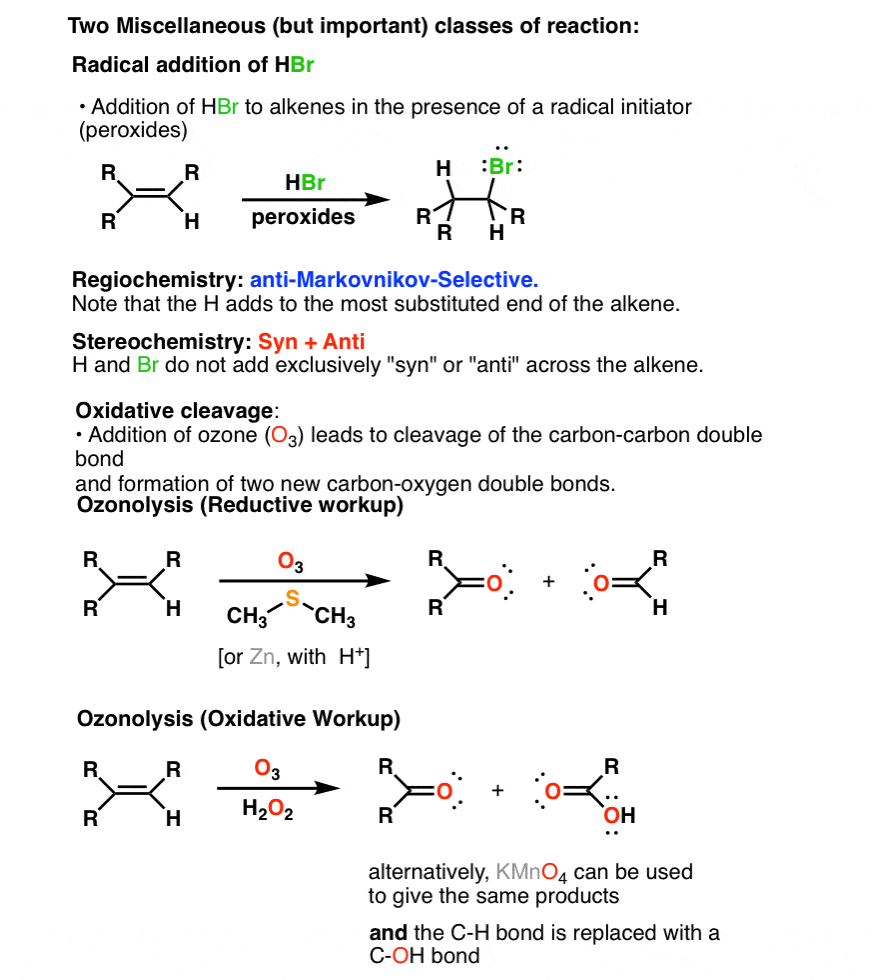
Summary Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms
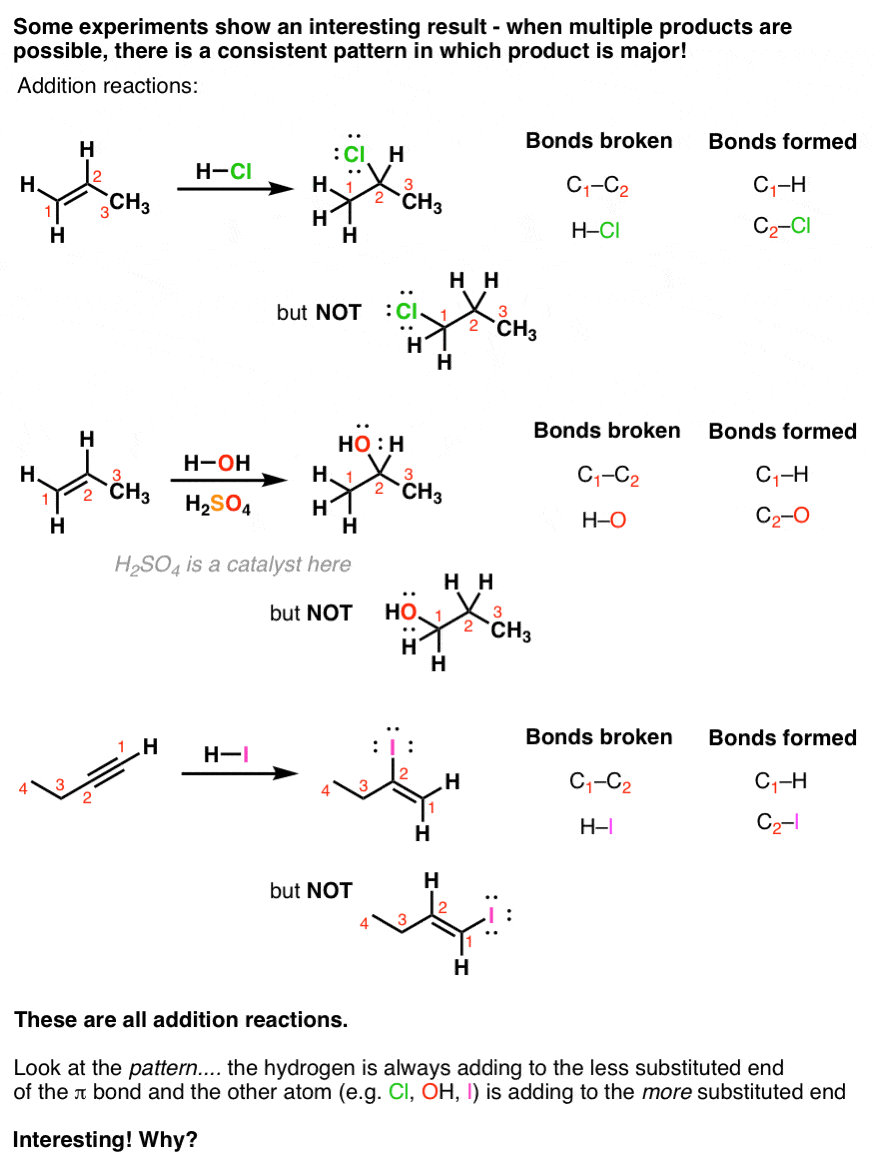
Introduction To Addition Reactions Master Organic Chemistry

Michael Addition Reaction Details Mechanism Examples Faqs
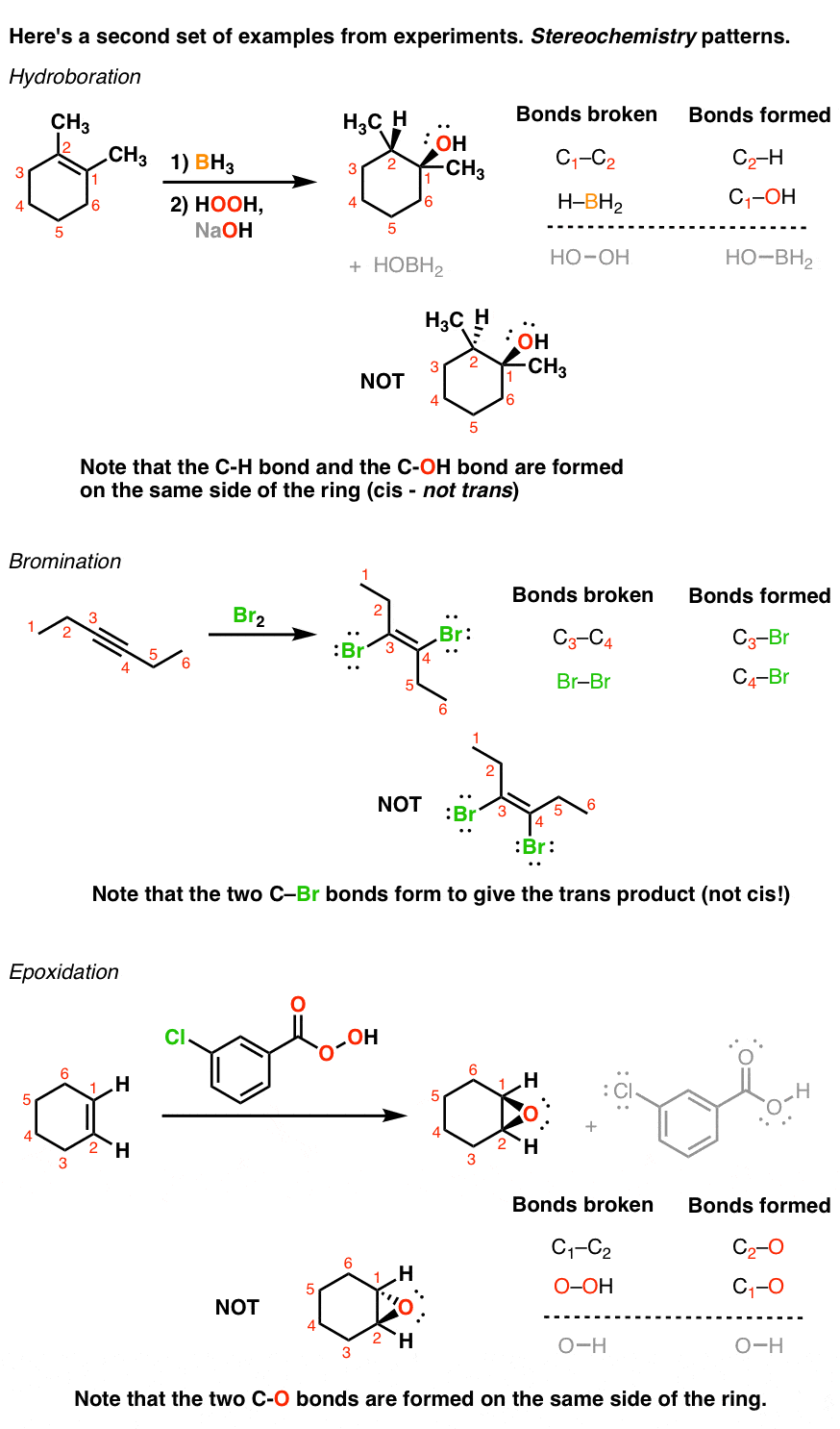
Introduction To Addition Reactions Master Organic Chemistry

Markovnikov S Rule Definition Explanation Of Mechanism With Examples

Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples

Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism
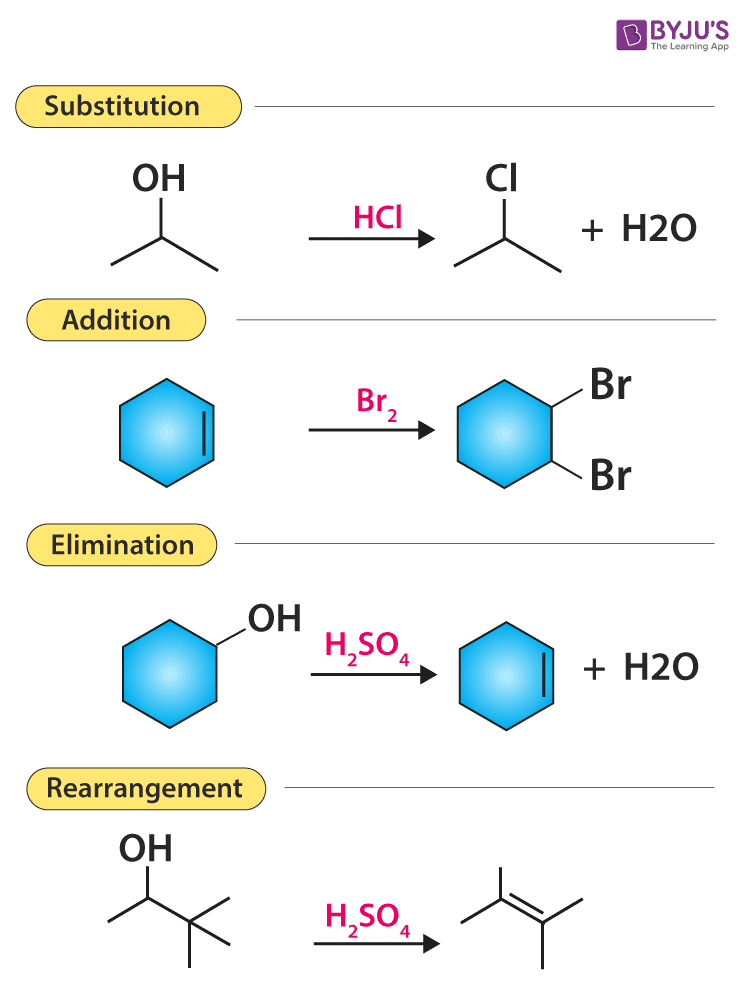
Various Types Of Organic Reactions Polar And Radical Reaction

Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism

Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism
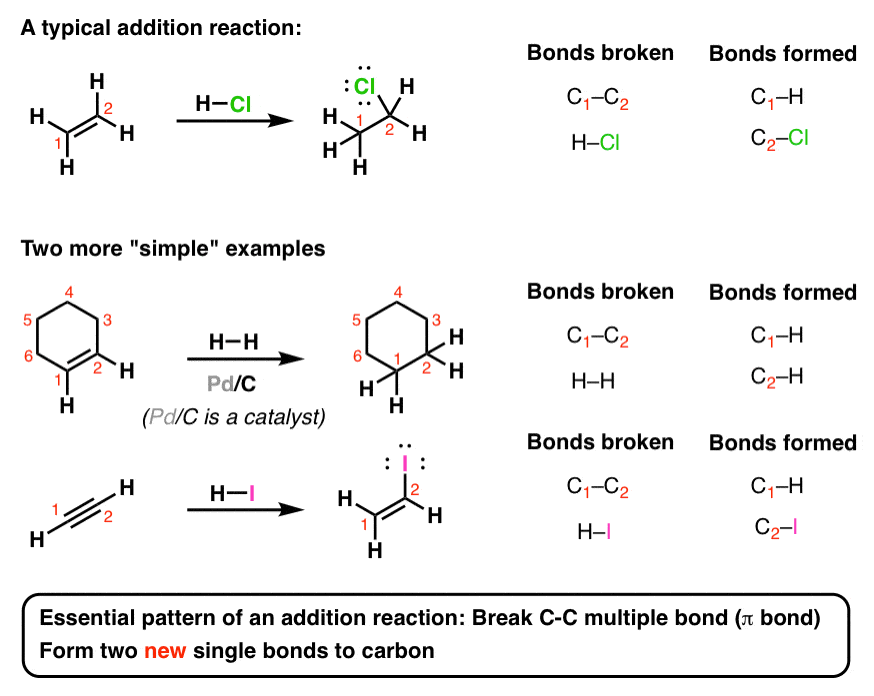
Introduction To Addition Reactions Master Organic Chemistry

Anti Markovnikov Addition Reaction Mechanism With Examples

Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples

Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism
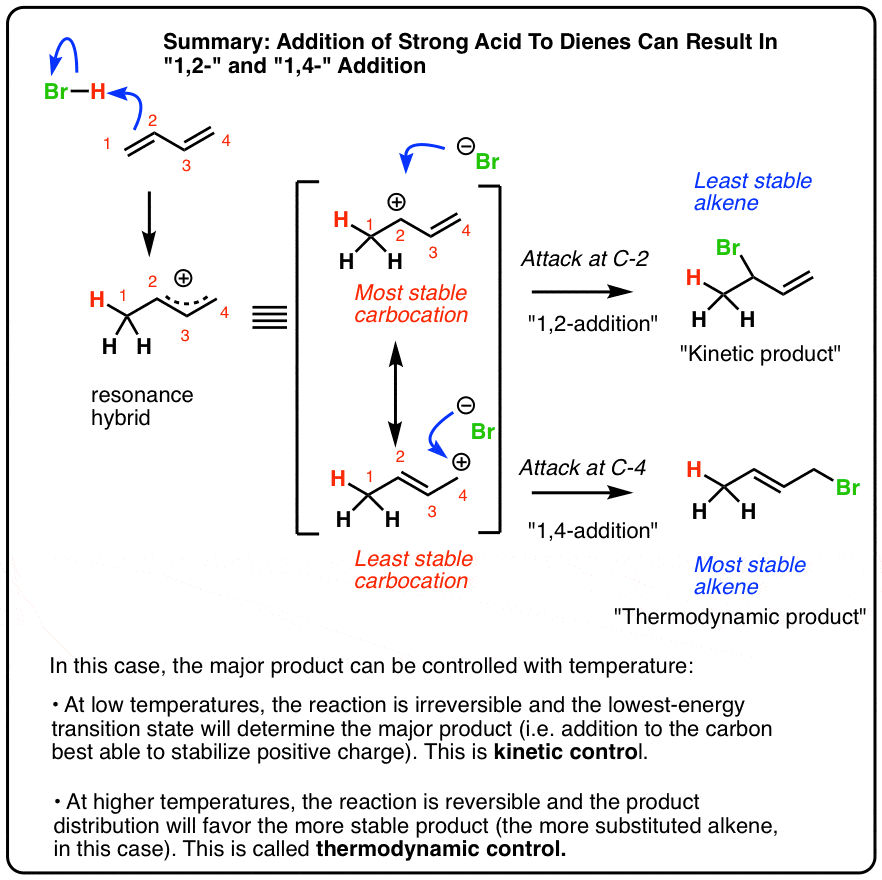
Reactions Of Dienes 1 2 And 1 4 Addition Master Organic Chemistry
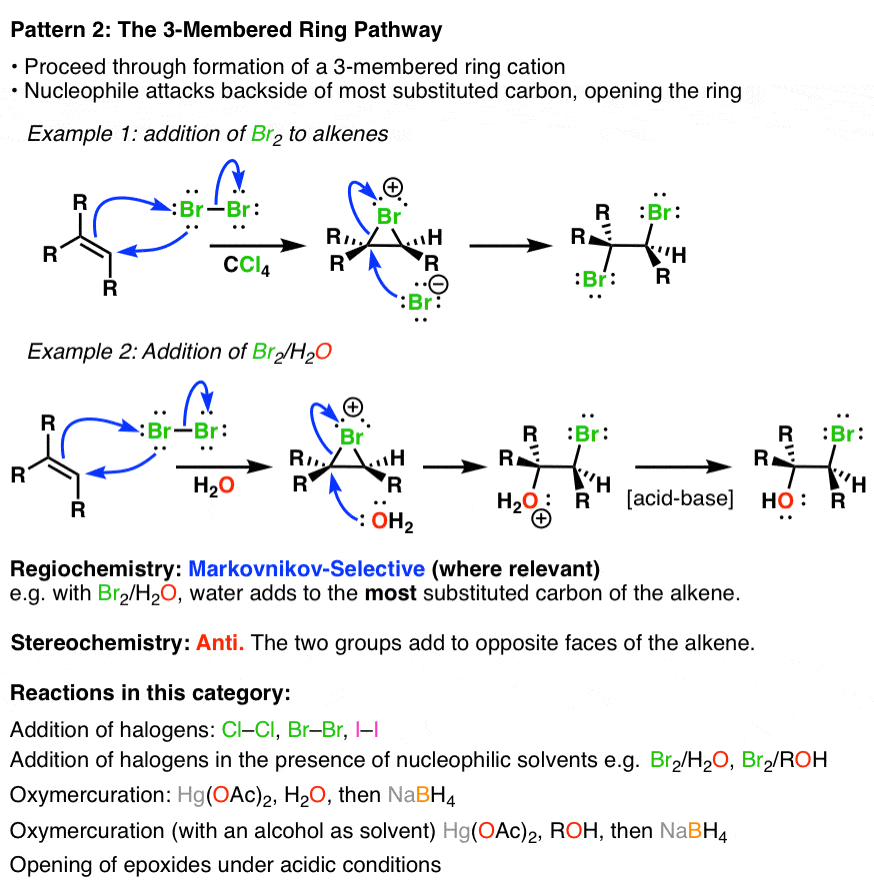
Summary Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms

Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
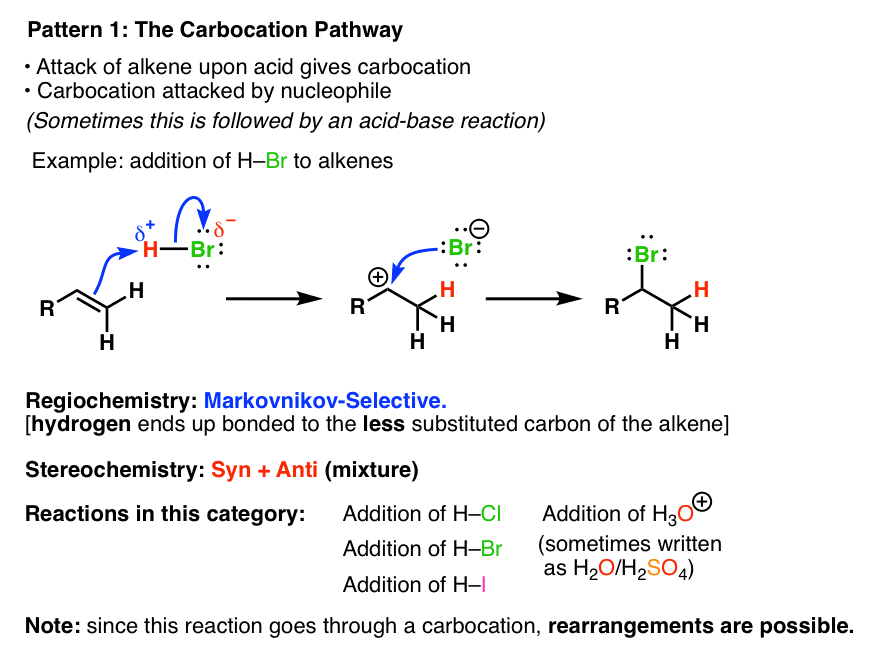
Summary Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms